Neural Modulation – Discover How Neurotransmitters Shape Sensory Responses

Understanding neurotransmitter modulation is crucial for grasping how substances influence brain and sensory function. Using a cricket's sensitive sensory system, this experiment demonstrates how substances like nicotine and MSG can dramatically alter neural responses, providing insight into the complexity of neurotransmitter action across different species.
About experiment
What Will You Learn?
- How sensory neurons respond to air vibrations.
- How inhibitory and excitatory substances modulate neural activity.
- The contrasting effects of neurotransmitter agents like MSG and nicotine on sensory neurons.
Background
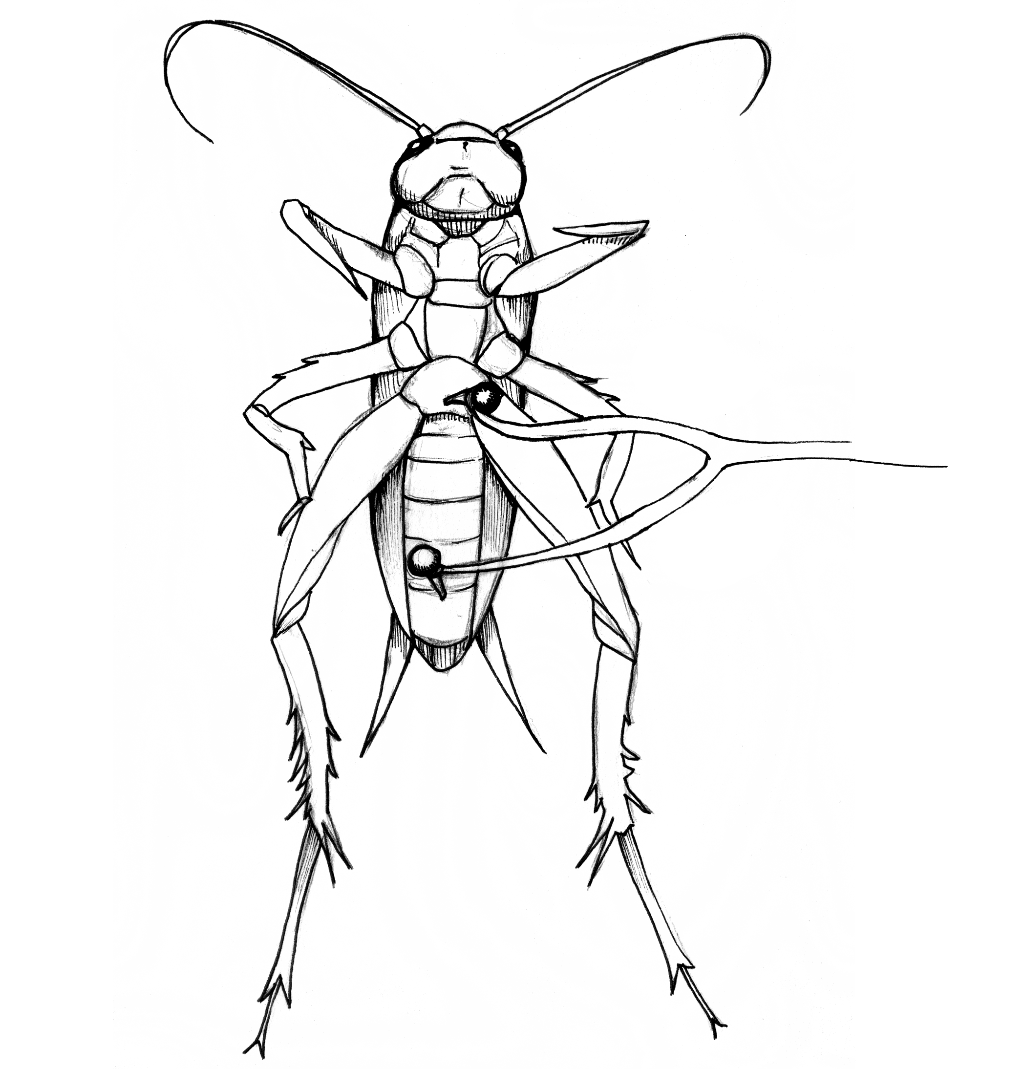
Crickets detect wind vibrations using cerci—specialized sensory organs sensitive to air movements. These cerci trigger neural activity that can be influenced by chemicals known as neurotransmitters. Interestingly, MSG typically inhibits neuronal activity in crickets, while nicotine usually enhances it, illustrating how neurotransmitters can have diverse effects in different organisms.
Procedure
Preparation:
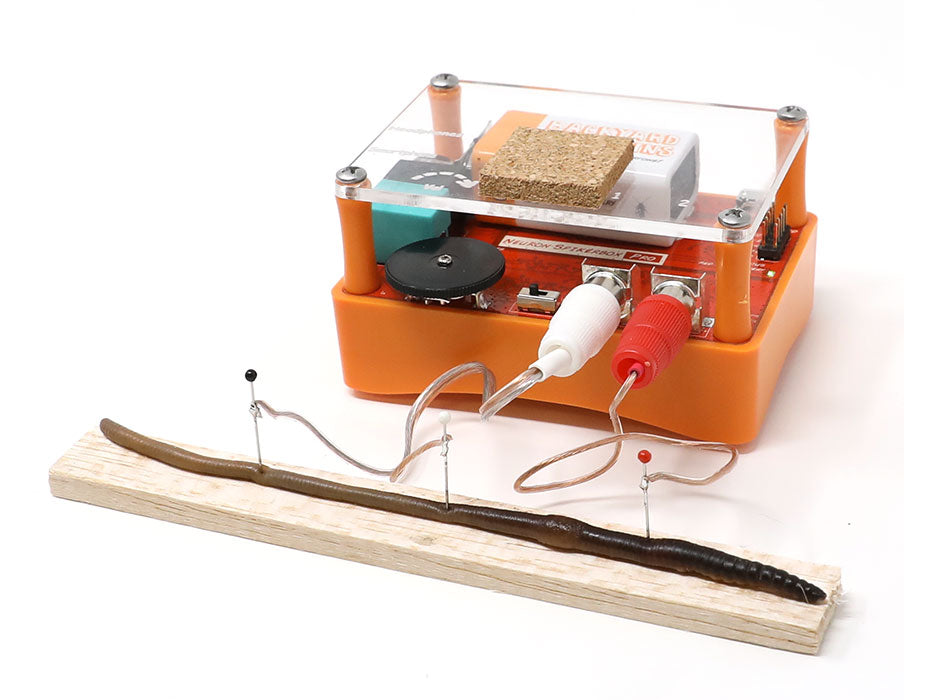
- Briefly anesthetize a cricket in ice water and secure it onto a stable platform without covering the cerci.
Electrode Placement:
- Place the recording electrode near a cercus.
- Position the ground electrode nearby, ensuring good contact with conductive gel.<./li>
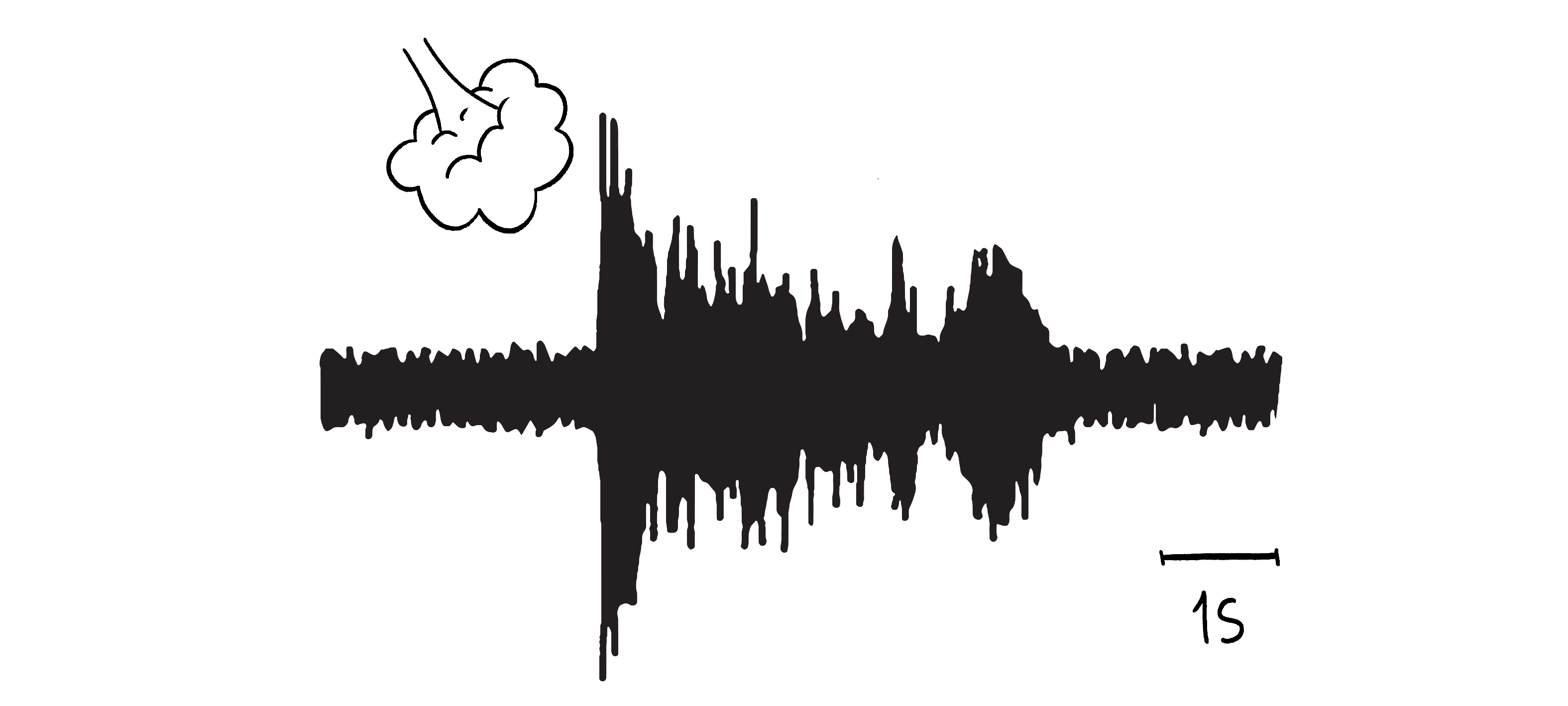

Baseline Recording:
- Record baseline neural activity using your Human SpikerBox.
- Stimulate cerci gently with air puffs to establish a baseline neural response.
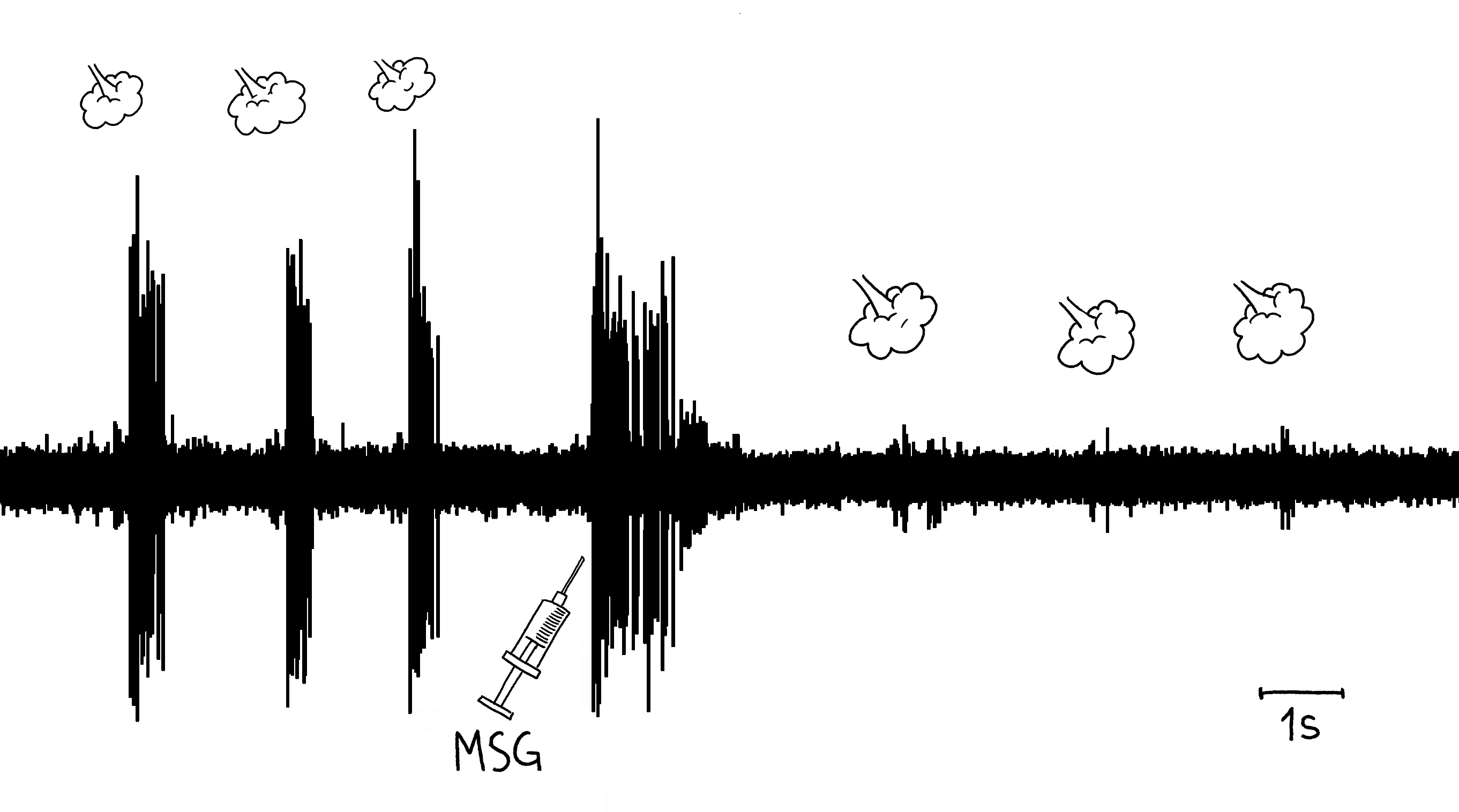
Neurotransmitter Testing:
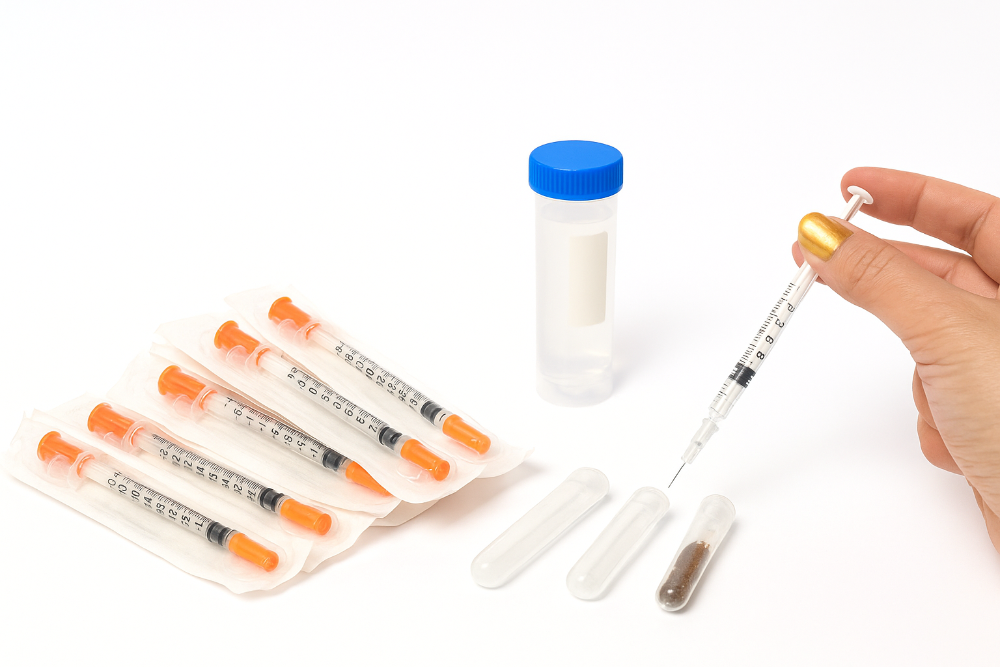
- MSG Application:
- Dissolve MSG in water and apply a small amount near the cerci.
- Record neural activity and compare with baseline.
- Nicotine Application:
- Prepare nicotine solution from soaked tobacco leaves
- Prepare nicotine solution from soaked tobacco leaves
Results & Analysis
MSG typically decreases neural activity, while nicotine usually increases activity.
Discuss potential reasons for the observed inhibitory effects of MSG and the excitatory effects of nicotine.
-
Related Products